DVD Demystified: What Does DVD Stand For?
Summary: When it comes to storing digital data like movies, music, and software, few technologies are as ubiquitous as the humble DVD. But what does DVD stand for, exactly? In this article, we’ll explore the basics of DVD, including its development history, working principles, current status, and future prospects.
Table of Contents

What Does DVD Stand For?
What is a DVD?
A DVD, or Digital Versatile Disc, is an optical storage device that can store large amounts of digital data. It was first introduced to the public in 1995 as a replacement for VHS tapes and quickly became the primary format for home video entertainment.
DVDs come in various sizes and can hold up to 4.7 GB of information on a single-sided, single-layer disc. With advancements in technology, dual-layer discs were later introduced, allowing for up to 8.5 GB of storage capacity.
The high storage capacity of DVDs made them ideal for storing movies, TV shows, music, and computer software. Additionally, DVDs offered improved picture and sound quality over VHS tapes, making them more appealing to consumers. DVDs also have additional features such as interactive menus, multiple language tracks, and subtitles, making them suitable for international distribution.
When did DVDs Come Out?
DVDs first hit the market in March 1997 in Japan and shortly thereafter in the United States. This new technology was a significant upgrade from the VHS tapes that were previously used for video recording and playback.
The development of the DVD format began in 1993, with the goal of creating a disc that could store more data than traditional CDs. The DVD’s increased storage capacity allowed for high-quality video and audio playback and the inclusion of interactive features like menus and bonus content.
Initially, DVDs were primarily used for movies, but as the technology improved, they became popular for other forms of media such as music, software, and video games. Today, DVDs are still widely used despite the increasing popularity of digital streaming services.

If you possess a substantial collection of DVDs and desire to backup their contents, you could consider utilizing the exceptional DVD Ripper and DVD Copy software to handle your DVDs with ease. These software tools facilitate the process of backing up your DVDs in an efficient manner, ensuring that your treasured DVD collections are safeguarded for future use.
How Do DVDs Work?
DVDs, work by using a laser to read and write data in the form of tiny pits and bumps on a disc’s surface. These digital discs can store large amounts of data, including movies, music, software, and other files.
The process of reading or writing data on a DVD begins with the spinning of the disc in the DVD player or drive. The DVD drive then shines a laser beam onto the disc’s surface, which reflects back to a sensor that reads the data encoded on the disc.
This data is encoded as a series of microscopic pits and bumps arranged in a spiral track from the center to the outer edge of the disc. The laser reads these pits and bumps as it moves along the track, interpreting them as ones and zeros that represent the stored information.
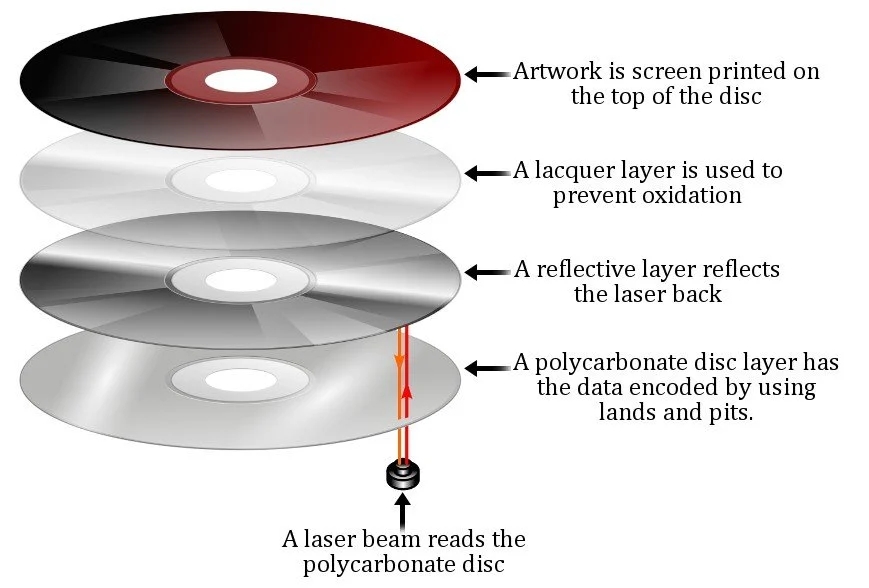
When it comes to writing data onto a DVD, the laser heats up a small portion of the disc’s dye layer, causing it to change its reflectivity properties. This creates the necessary pits and bumps that encode the data onto the disc.
DVD Takes Over the World
In the late 1990s, DVDs hit the market and quickly became the preferred format for home entertainment. With their superior image and sound quality, compact size, and interactive features, DVDs took over the world of home media.
The rise of DVDs was fueled by a number of factors. First, the format offered significant improvements over VHS tapes, which were bulky, low-quality, and prone to degradation over time. DVDs also had a smaller form factor, making them easier to store and transport. Additionally, DVDs offered advanced features such as scene selection, bonus content, and multiple language tracks, making them more versatile than any other home media format at the time.
As the popularity of DVDs grew, so did the market for DVD players. By the early 2000s, DVD players had become affordable and widely available, with many models offering additional features such as progressive scan and upscaling to improve picture quality on high-definition TVs. This made it easy for anyone to enjoy high-quality home entertainment without breaking the bank.
DVDs also had a significant impact on the film industry, with studios using the format to release new and classic movies alike. DVDs offered an opportunity for studios to generate additional revenue through the sale and rental of their films, as well as through the inclusion of special features and bonus content that could not be found anywhere else.

While DVDs eventually gave way to digital streaming, their impact on the world of home entertainment cannot be overstated. The format revolutionized the way we watch movies and TV shows, and paved the way for the high-quality home media options that we enjoy today.
The Future of DVDs
With the rise of streaming services and digital downloads, it’s fair to wonder what the future holds for DVDs. However, despite the convenience of these new technologies, DVDs are not going anywhere anytime soon.
One of the main reasons for this is that many consumers still prefer physical media. DVDs offer high-quality video and audio, as well as special features and bonus content that can’t be found on streaming platforms. Additionally, owning a physical copy of a favorite film or TV series allows for a sense of ownership and collection that digital media can’t replicate.
Furthermore, DVDs have proven to be a reliable format for long-term storage. Unlike digital files, which can be lost or corrupted over time, DVDs can last for decades when properly cared for. This makes them an excellent choice for archiving important family videos, home movies, and other precious memories.
As technology continues to evolve, DVD players are also becoming more versatile. Many newer models now feature smart capabilities, allowing them to access online content and stream from services like Netflix and Amazon Prime. This means that even if DVDs do eventually become less popular, people will still be able to enjoy them on modern devices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while there may come a day when DVDs are no longer the dominant format for home entertainment, they will always have a place in the hearts of cinephiles, collectors, and anyone who values quality and reliability. So, whether you’re starting a new collection or just looking to preserve your existing one, DVDs are here to stay.