DVD Formats Explained: Types, Compatibility, and Best Choices
Summary: Choosing the right format can be confusing when faced with so many DVD options, such as DVD-R, DVD+R, DVD-RW, DVD-RAM, and DVD-ROM. Each serves different recording and playback purposes depending on your device and usage scenario. This guide breaks down every DVD format’s features, compatibility, and ideal use case so you can pick the most suitable one for backing up, authoring, or watching DVDs today.
Table of Contents
When I tried to burn an old home movie onto a blank disc, I was surprised to find several types of DVDs. Each looked identical, yet only one worked with my DVD burner. That experience made me realize how confusing DVD formats can be, especially when compatibility differs from one device to another.
If you've ever wondered which DVD format works best for recording, playback, or data storage, this guide will make things clearer. In the following sections, I'll explain the differences among all major DVD types, how they affect performance and compatibility, and which one you should use depending on your needs, whether that's burning videos, creating backups, or preserving movie collections.

Quick Answer: Which DVD Format Should You Use
- Best overall: DVD+R - reliable, widely supported, easy to find.
- For old players: DVD-R - home-video authoring, better legacy compatibility.
- For reuse: DVD-RW - suitable for test burns or temporary data.
- For data backup: DVD-RAM - most robust but niche.
Below is a quick reference guide comparing the main DVD formats you'll encounter. Each format differs in write capability, reusability, compatibility, and ideal usage scenario.
| Format | Writable | Rewritable | Typical Capacity | Playback compatibility | Availability |
| DVD-R | Yes (once) | No | 4.7 GB SL / 8.5 GB DL | Very high on older players | Widely available |
| DVD+R | Yes (once) | No | 4.7 GB SL / 8.5 GB DL | Supports bitsetting for broader playback | Widely available |
| DVD-RW | Yes | Yes (~1,000 cycles) | 4.7 GB | Moderate, some old players picky | Still produced |
| DVD-RAM | Yes | Yes (1,000+ cycles) | 4.7 GB | Low in set-tops, great in PCs | Limited |
| DVD-ROM | No | No | 4.7 GB / 8.5 GB | Universal (pressed) | Factory only |
Overview of Major DVD Formats
DVD-R
DVD-R (Digital Versatile Disc Recordable) is a generic recordable DVD format that looks like a traditional DVD but allows information to be written only once and read multiple times. DVD-R is a DVD format that is compatible with all recordable DVD formats. It can store up to 4.7 GB of information or media records on a primary disk and up to 8.5 GB on a double-layer disk. A disc can only be used once and cannot be used for re-recording whenever it is removed from the drive.
DVD+R
Released in 2002, described as DVD Plus R. It is a recordable DVD format similar to DVD-R but does not carry the DVD logo. It uses the ADIP method and is usually slightly more expensive than DVD-R. Playback compatibility with all DVD players has been improved to approximately 80%.
Quick tip: If your burner supports bitsetting, always enable it when using DVD+R—this can dramatically improve playback success across older devices.
DVD-RW
DVD-RW allows data or video to be erased and rewritten up to 1,000 times, making it practical for temporary storage or testing projects before final burning. It is backward compatible with many (but not all) DVD players. The disc's reflectivity is lower than that of DVD-R, which can sometimes cause playback issues on older players.
DVD-RAM
DVD-RAM is the most technically advanced of all recordable formats. It supports true random access, built-in defect management, and an exceptional rewrite lifespan (up to 10,000 cycles). This makes it extremely reliable for data backup, professional archiving, and video recording devices like Panasonic camcorders or set-top recorders. However, DVD-RAM discs are not compatible with most standard DVD players or drives, and their availability has declined in recent years.
DVD-ROM
DVD-ROM is the factory-pressed, read-only format used for commercial movies, games, and software distribution. These discs cannot be burned or modified. Their universal compatibility makes them the standard for pre-recorded media. Every DVD player and drive can read DVD-ROM discs without issue.
While all DVD formats share the same disc size and storage capacity, their write behavior, reusability, and compatibility differ significantly. For everyday use, DVD+R remains the most reliable and available option, whereas DVD-RAM continues to lead in durability for archival storage.
Physical vs Logical DVD Formats
When people talk about DVD format, they often mix up two very different concepts: physical formats and logical formats. Understanding this distinction helps explain why two DVDs that look identical can behave very differently when you try to play or copy them.
Physical DVD Formats: The Disc Itself
The physical format refers to the type of disc you can hold in your hand, such as DVD-R, DVD-RW, DVD-RAM, or DVD-ROM. Each type determines how data is recorded onto the disc's surface, whether it can be rewritten, and how compatible it is with different drives.
DVD-R or DVD+R can store video, audio, or any digital data, but they serve merely as a carrier and are not the content format itself.
Logical DVD Formats: The Data Structure
The logical format defines how the data is organized and read by a computer or player.
Two main logical formats exist:
- DVD-Video: Designed for film playback, it uses a specific folder structure (VIDEO_TS and AUDIO_TS) and the UDF 1.02 file system. This format is recognised by DVD players, ensuring smooth playback of menus, subtitles, and chapters.
- DVD Data Disc: Used to store general files such as videos, documents, or images, similar to a USB drive. It usually uses UDF 1.5 or higher, which allows larger files and modern encoding formats.
File Systems Used in DVDs
DVDs can use several file systems to organize data:
- UDF (Universal Disc Format): The standard format for most DVDs; DVD-Video uses UDF 1.02, while large data files or Blu-ray compatibility require UDF 2.5 or higher.
- ISO 9660 and Joliet: Traditional formats retained for backward compatibility with legacy PCs. Modern authoring tools often employ a hybrid UDF/ISO structure to ensure discs are readable on both computers and set-top box players.
Understanding the physical and logical characteristics of DVD formats eliminates most playback and burning issues, ensuring discs perform as intended on any device.
Convert and Preserve Any DVD Format
Even the most reliable physical DVD formats have a finite lifespan. Over time, discs may become unreadable due to scratches, oxidation, or drive compatibility issues. The optimal way to safeguard your collection is to convert DVDs into digital files. DVDFab DVD Ripper provides a comprehensive solution for this purpose.
DVDFab DVD Ripper can read and convert any DVD format into high-quality digital files such as MP4, MKV, AVI, MOV, or WMV. It automatically removes region codes, CSS encryption, and copy restrictions. The software also supports multi-core CPU, GPU acceleration, enabling faster conversion speed without compromising quality.
- Convert DVD disc, ISO, or folder into popular video and audio formats
- Select from lossless or high-quality compressed outputs
- Customize output with built-in video editor and advanced settings
- Output optimized profiles for TV, mobile, and home theater playback
How to Digitize Your DVDs Using DVDFab DVD Ripper
Step 1: Install DVDFab DVD Ripper and choose the ripper module. Insert your DVD disc into the optical drive, or load a DVD ISO/folder by drag-and-drop or through the "Add" button.
Step 2: Open the Profile Library to select the format you want to convert to. You can choose from a variety of options, depending on where you plan to play the video. Each format includes multiple device-optimized profiles for TVs, smartphones, or tablets.
Step 3: If you want to customize the video, open the Video Editor or Advanced Settings panel. Here you can trim or crop clips, adjust brightness or contrast, change resolution or bitrate, and even add watermarks before ripping.
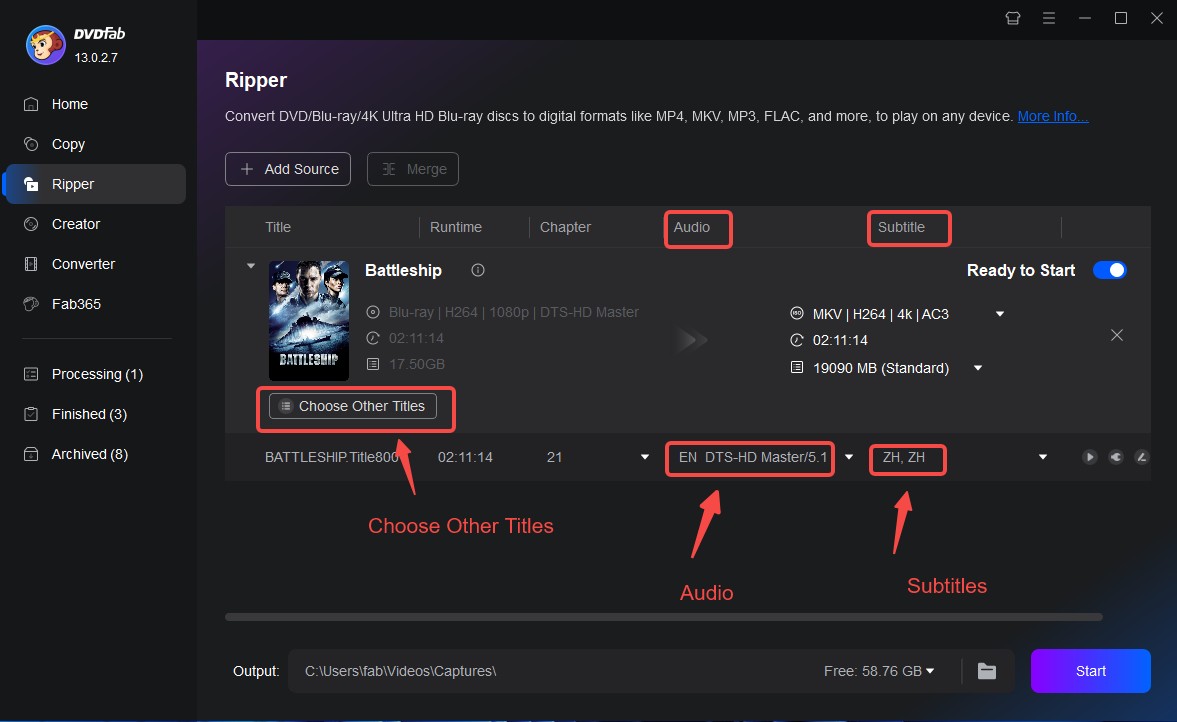
Step 4: Click Start to begin the ripping process. DVDFab will display the real-time progress bar. Once complete, you can set the program to shut down, hibernate, or remain open.
Conclusion
Understanding the different DVD formats helps you choose the right disc for recording, playback, or archiving. While physical media still serve valuable purposes, their lifespan and compatibility are limited. To ensure your movies, data, and memories remain accessible, converting discs to digital files with DVDFab DVD Ripper is a long-term solution. It keeps your collection secure, and free from the constraints of aging DVD formats.

![Top 3 Ways to Compress ISO Files Losslessly [2025 Updated]](https://r5.dvdfab.cn/upload/resource/en/compress-iso-Fexa.jpg)


